Namaskar! My name is Rupesh Jadhav and welcome to Rupeshfinancialexpert. where I don’t lock, rather unlock the knowledge of finance. This blog is a part of the series in which is I am writing negotiable instruments. I have already mane few blogs related to promissory notes, bill of exchange, and cheques. If you haven’t read them then make sure to read them. In this blog, we’ll discuss types of bills of exchange. In the bill of exchange blog, I had discussed the demand bill and usage bill. So, in this blog, we’ll understand both these bills in detail. Also, we’ll divide the rest of the bill of exchange into various categories and will check what kind of bills of exchange are there? for example, trade bills, accommodation bills, or order bill or bearer bill. In-land bill or foreign bill. We’ll understand all these types of bills in this blog. So, make sure to read it from the start to last.
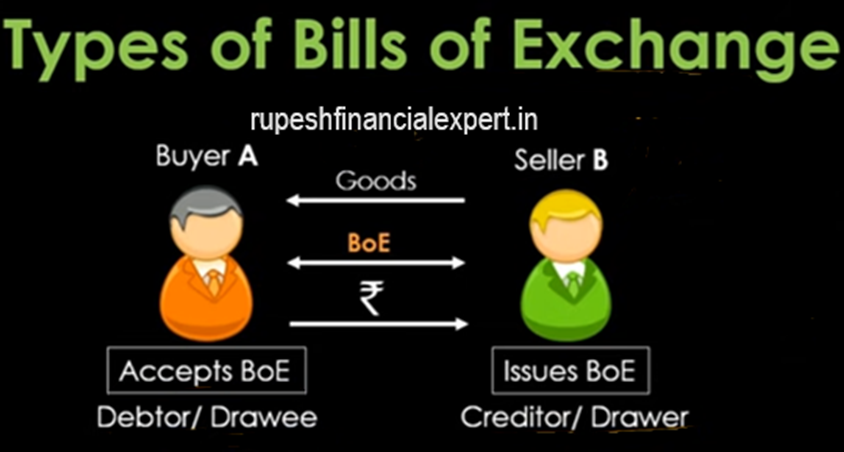
So let’s understand in this blog, how many types of bills of exchange are there? First, let’s summarize bills of exchange one time. I have already made a detailed blog on it. Still, let’s do a quick recap. suppose a buyer A who has to buy some goods from seller B. It says I don’t have immediate money, Give me the goods on credit. I will make your payment after 2,3 or 4 months, whenever I have the money. Seller B thinks that his relations are good, buyer A is a regular customer of his. So he gets ready to give the goods on credit, and he delivers the goods on credit. But he also says that sign a bill of exchange with me. Bill of exchange is a kind of financial instrument in which all the details are written that buyer A is agreeing to give money to seller B.
On a certain date or whenever the seller needs it, the buyer will give the money. One who issues the bill, he is the seller, or we call it the creditor, because he is giving it on credit. Or because he is drawing the bill of exchange, we call it a drawer too. and accepting the bill of exchange is necessary, so until the buyer accepts it, it won’t be considered valid. Also, because he is taking the credit, we call it debtor, and we call it drawee. because the bill of exchange is issued in its name. so this is the working of the bill of exchange in short.
Now let’s check how many kinds of bills of exchange are there. I’ll categorize them in different ways. If we categorize by time period, so, one is your demand bill or which we call sight bill too. and second is your Usance bill or which we call term bill also. The demand bill is basically payable, whenever the seller demands it or whenever he presents it. So, in this case seller is the payee. Now there can be another third party besides seller B. suppose there is a creditor of seller B, let’s say party C. and if the seller endorses it in the name of party C, so whenever C presents it, then the buyer has to make the payment. So basically, demand bill is payable, when it’s demanded or presented.
The date can be or not. The maturity date may or may not be there. for example, the maturity date is written in the bill, whenever seller B will demand the money, so the buyer has to pay within 4-5 days. So, if i take an example, how it is written? On-demand, pay to Mr. XYZ, XYZ is the seller or any payee which the seller endorses. or to order a sum of Rs. 1,00,000 for value received. So, whenever XYZ demands, or its order, order means either its endorsement is done. that third party if demands the money then the buyer has to give Rs. 1,00,000. so, this is the demand bill.
Second is the Usance bill or term bill. This specifically matures on a future date, on which date the payment has to be done. So, the exact mature date or due date is written. On that day buyer has to do the payment to the seller or any third party, whom seller B endorses. If I take its example, then it’s written like 60 days from date, date means, whenever the bill is executed. Pay Mr. XYZ or to order or its third party or whoever he is making the nominee. a sum of 100,000, for value received. So clearly, the date is mentioned. The date whenever it is executed, after 60 days of that, the payment has to be done. So, in it exactly the date is given in usance or term bill.
Now let’s understand the categorization of bills of exchange in a different way. If i want to define it by purpose, then it is defined in two ways. One is your trade bill and the second is the accommodation bill. Trade bill is the same where exchange of the goods happens. So, whenever a trade or sale and purchase of goods happen. So, we call it the trade bill. which i discussed, whether it’s demand bill or usance bill. Now like goods are being traded in the trade bill in accommodation bills, the goods are not traded. and no consideration is passed in this bill. Generally, they give each other debt and return it, for this accommodation bill is signed.
So generally, it’s used for fundraising. Assume B gave some money to A as debt. They signed a bill of exchange. And after some time, A returns the money to B. so, when parties have short term fund requirements between them. in this way, they can match by signing the accommodation bill. So, in the same way, assume B got the bill of exchange, so through it, by doing bill discounting B can raise money from the bank too. If you haven’t read the bill discounting Blog, then Read it. You’ll understand how funds are raised through bill discounting. So, these were the trade bill and the accommodation bill.
In what other way we can categorize? We can also categorize them by place. One is your inland bill, and the other is the foreign bill. Inland bill, as the name suggests, in the same country, it is traded so we call it the Inland bill. In this case, the drawer and drawee, means the buyer and seller, both are in the same country. In a foreign bill, basically, it’s drawn in one country and payable in the other country. So, it’s possible that this buyer A might be importing some goods in India, and seller B might be in China, for example. we call it a foreign bill when two countries are involved in import and export. So, in foreign bill drawer and drawee are in different countries.
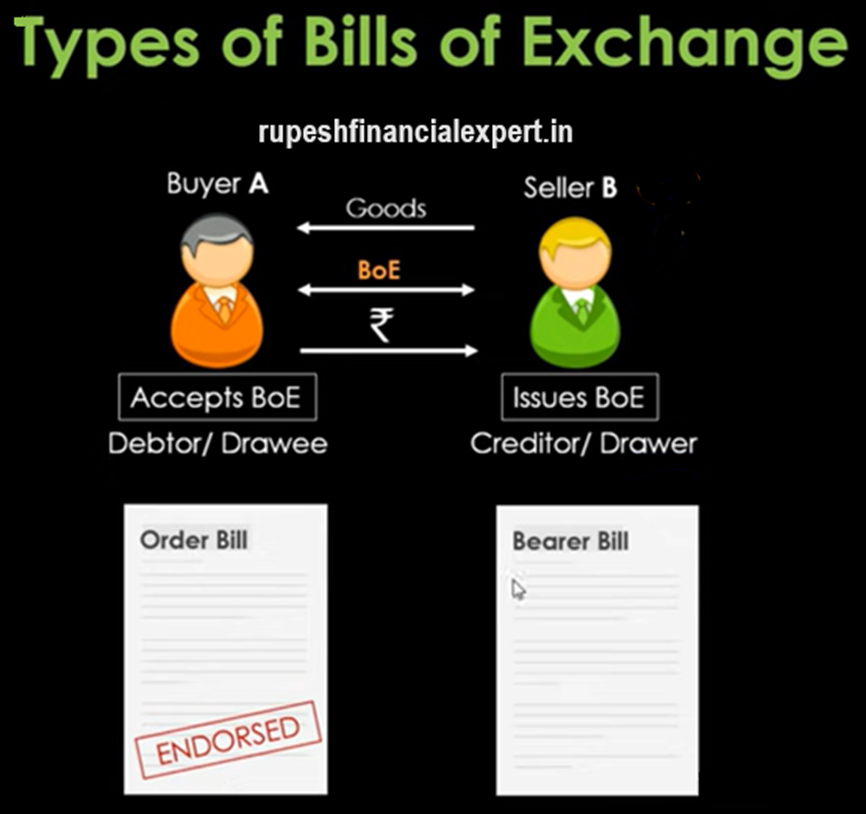
Now next categorization can happen by parties. Means what parties are involved in it or who can encash it? so in this, one is the order bill and the second is the bearer bill. Now, what is the order bill? I’ve already discussed the order bill. So, basically this is paid to a specific person, whose name is appearing on this bill. So, whoever’s name will be written on the bill, it’ll be paid to him. So, it means that the seller or we can call it the drawer, it’ll be paid to either him or its endorsee which I talked about the third party. If he endorses to any C party, then it can be paid to him. So, if we say order bill, there is an endorsement, it is endorsed like that, and in favour of C, it is executed, which means the payment has to be done to C. so if we see its language, how is it written? 60 days from date pay Mr. XYZ or to order, means Mr. XYZ, whoever’s name he writes or whoever he endorses, he has to be given Rs.1,00,000.
On the other hand, through bearer bill, the payment can be done to any person, whoever has the bill, he can collect the money. There is no need for any endorsement in this. Assume B hands over this bill to C. so, this C, by showing the bearer bill, can collect the payment straight up. If I take its example. So, it’ll be written 60 days from date pay Mr. XYZ or to bearer, means whoever holds the bill has to be given Rs. 100,000. So, the only difference is in language, ‘or to order’ is written, and ‘to bearer’ is written’. which means whoever has the bill, will get the payment.
Now let’s check at the categorization in a different way, by documents. There are two bills in it, the first is documentary bill and the second is clean bill. Let’s understand both. In the documentary bill, there are two kinds of the documentary bill, one is the documents against acceptance bill, in this the seller, basically, first of all, the seller sends the D/A bill with documents to the buyer. and which documents are these? like the bill of lading, consular invoice, certificate of origin, marine insurance or air insurance, anyhow the cargo is traveling and the rest of the invoice. So, all these documents are sent with the bill of exchange. So, as the bill of exchange is going, documents are also sent within the D/A bill. So, first of all the buyer has to accept the bill of exchange. After the acceptance, the documents are handed over. In the second step, these documents are handed over to buyer A. In the third step, all the goods are delivered. first of all, the buyer accepts, then documents are handed to buyer A by the seller. In the third number, goods are handed over. After that, finally payment will be done according to the bill of exchange. this is the fourth step; payment will be done as per the maturity date. So, this was the documents against acceptance bill.
The second is our documents against the payment bill. What happens in documents against payment bill? So, first of all he will definitely accept the bill of exchange. Nothing can be done before that. Like in the first case, documents were being handed over, in this case, he will do the payment on the second number. He accepted the bill of exchange first, then he will accept the payment. after that, the documents will be handed over to the buyer. On the third number, he will get the documents. When he does the payment to the seller then the documents will be handed over. and after that, he will get the goods on the fourth number. so, in this, you get the documents only after the payment. and then he can collect the goods. So, this is the difference between documents against payment and documents against acceptance.
So, these were the documentary bills if we talk about the documents. Then the second is your clean bill. In a clean bill, any kind of documents are not sent through bill of exchange. So basically, through only bill of exchange your goods are delivered. And when bill discounting is done then higher interest is charged on the clean bill, because whenever there is documentary evidence, banks give money easily. As I said before, I’ve made a detailed Blog on bill discounting. so, you can read this Blog of bill discounting. so basically, what happens in bill discounting? You raise funds through the banks. suppose seller B is getting a very late payment from the buyer, he will go to a bank and after discounting the bill, he will collect the funds on basis of that bill of exchange. So, in the clean bill, the interest rate charged on the funds given by the bank, is basically charged more in the case of a clean bill. In the case of the documentary bill, the interest rate is charged a bit less. So, this is the difference between a documentary bill and a clean bill.
Now let’s check at some other types of bills of exchange. Basically, in India Hundies were used in the old times. these informal bills of exchange were used in India. But even today these are used in some informal places, but they have no legal status. and these are not covered under the negotiable instrument act 1881. But all the other types of bills of exchange I discussed with you, are legal and are covered under the negotiable instrument act 1881. So, by chance if your payment is not done, then you can file a suit against the buyer.
So, I think I’ve covered all types of bills of exchange. I hope you enjoyed this Blog, so do comment and share it. If you have any suggestions or you want to suggest topics for the future Blogs, then you can do it in the comment section below. I read all of your comments regularly and I try that maximum topic. I can share through Blogs. So, do maximum topics and tell me which topics should I cover? I share finance and investment-related very interesting topics on this website. So, let’s meet in the next Blogs.
Till then keep learning, keep earning, and be happy.