House Rent Allowance (HRA) is a valuable tax benefit for salaried individuals residing in rented accommodations. As per Section 10(13A) of the Income Tax Act, employees can reduce their taxable income by claiming HRA exemptions. With the latest budget updates affecting tax planning, understanding the eligibility criteria, documentation requirements, and best practices is crucial for maximizing savings.
Understanding HRA Exemption: The Calculation Method
The HRA exemption is determined based on three key components:
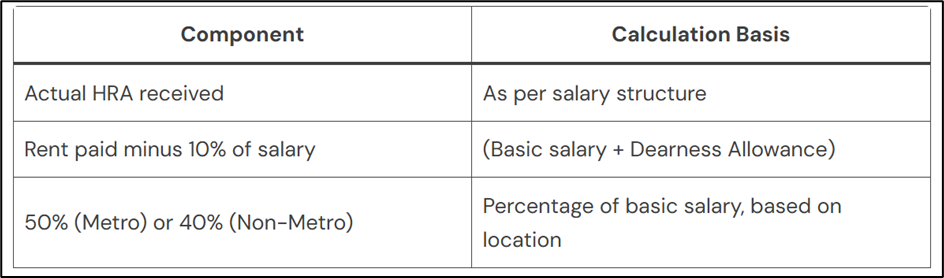
The lowest of these three values is considered the HRA exemption, while any remaining HRA is taxable.
Did You Know? The 2025 tax law is more concise than the 1961 Act, with only 536 sections across 622 pages compared to the old Act’s 823 pages.
What’s New in the 2025 Budget?
- Higher Standard Deduction: The new tax regime now includes a standard deduction of ₹75,000, but HRA exemption is only applicable under the old tax regime.
- Stricter Documentation Requirements: If your annual rent exceeds ₹1 lakh, providing your landlord’s PAN is mandatory.
Best Practices for Claiming HRA Tax Benefits
Dos:
- Maintain rent receipts and agreements: Rent receipts are necessary for claims exceeding ₹3,000 per month.
- Prefer digital transactions: Paying rent via bank transfer, UPI, or cheque ensures a verifiable money trail.
- Accurately declare landlord details: If rent exceeds ₹1 lakh annually, the landlord’s PAN details must be submitted.
- Leverage both HRA and home loan benefits: If you own a home in a different city, you can still claim HRA along with home loan interest deductions.
- Evaluate tax regimes: Compare the old vs. new tax regimes to determine the most beneficial option.
Don’ts:
- Avoid cash payments: Untraceable rent payments may lead to claim rejection.
- Don’t claim HRA for non-existent rent payments: False claims can lead to severe penalties.
- Be cautious with family rentals: If renting from a family member, ensure the landlord declares rental income in their tax returns.
- Never skip rent agreements: An outdated or missing agreement may cause tax filing complications.
Optimizing HRA for Maximum Savings
- Metro advantage: If you reside in a metro city, your HRA exemption can be higher (50% of basic salary instead of 40%).
- Compare with the standard deduction: If your total deductions (HRA + 80C + 80D) exceed ₹75,000, the old tax regime may provide better tax savings.
- Seek professional advice: Consulting a tax expert can help you structure your salary optimally and claim exemptions legally.
Final Takeaway
HRA continues to be a crucial tax-saving tool for salaried individuals. However, with the new tax regime eliminating HRA exemptions, selecting the right tax structure is vital. By following the correct steps and avoiding mistakes, you can maximize your tax savings while staying fully compliant.
Disclaimer
The information in this article is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, tax, financial, or professional advice. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, tax laws may change, and individual circumstances differ. Readers should consult qualified professionals or official government resources for personalized guidance. The author and publisher are not responsible for any decisions or actions taken based on the information provided.




