Namashkar, My name is Rupesh Jadhav and welcome to Rupeshfinancialexpert, where I unlock the knowledge of finance rather locking it, When an international trade takes place and importer and exporter don’t know each other, There is a trust issue In this case, there can be 2-3 ways through which payments can be paid or received, in that one way is a documentary credit which is also called the letter of credit, I made a detailed blogs on this, so if you haven’t read it then do read it.
2nd way is the documentary collection method, In the documentary collection method, there are 2 methods.
1. Documents against payment
2. Documents against acceptance

I’ll understand these 2 methods in detail in this blog, and we’ll understand a flow chart on how the whole workflow goes, so read till the end to get the concept properly.
Firstly, let’s check, what is the process of payments in export and import, Let’s check this is an exporter from China and an importer from India, Importer wants to buy some goods from the seller, There is a trust issue between both Seller, thinks of sending the goods first without payment, And the importer thinks what if I don’t get the goods after paying the money, That’s why they rely on the banking system, Exporter relies on his bank and importer on his bank, and because the banking system is very robust in the international banking system, So there is a trust between them, So a remittance bank and this is a clearing or presenting bank, So the payment can be done through these 2 banks, The first method is documentary credit which is also called letter of credit (LC), So I have already written the method of letter of credit, and I already made a detailed blogs, So you can read that blogs.
Second is the documentary collection method, there are 2 types of methods in the documentary collection.
1. Document against payment
2. Document against acceptance
Both of these are kinds of bill exchanges, so document against payment is the site bill of exchange, as this bill of exchange will be presented in front of the importer, the importer has to do immediate payment, and document against acceptance bill is a type of Usance bill, which provides a time period to the importer to do the payment, so both the methods are used. It depends on what suits the importer, if he has money in advance, and he can give some immediately, then he can go with the D/P bill. Otherwise, if he needs some credit period, then he can go with the D/A bill, Now let’s see how both of these methods work and let’s understand their workflow.

Firstly, let’s understand the common process of the documentary collection, Firstly, a sales contract is signed between the exporter and the importer, they pre-decide through which method they will go , So as I told you before, immediate payment is to be done by the importer as soon as this DP, will be presented in front of the importer, And in DA, you get a time period because this is a Usance bill, So I already made a detailed blogs on types of bills of exchange, So if you haven’t read it then you can read it, you’ll get to know more about the site bill and usance bill.
So, this was the first sales contract, In the first process, the sales contract is signed between the exporter and importer, In the second step, the exporter will ship the goods towards the importer, that means towards the port of the importer’s country. But definitely, it didn’t reach the port, Once the goods are shipped, the exporter will prepare the documents, In the documents, bill of exchange is there, Then there is the bill of lading which is a very important document, I made a detailed blogs on the bill of lading, so you can read that blog, You’ll get to know what all documents are required Also, I made a detailed blogs on Incoterms.
These are the international commercial terms, international trade is done according to it, so you can read my Incoterms blog, Basically, when the exporter will prepare all these documents, like the bill of exchange, bill of lading, invoices, trade documents. So, he will go to the remitting bank and will transfer the documents, So the exporter is relying on his bank, after that, the remitting bank will check all the documents, and will pass the instructions to the collecting bank, which is there in the importer’s country. So, the collecting bank can be a branch, or associate of the remitting bank, Presenting bank can be separate, or collecting and presenting banks can be the same, So the presenting bank can be a separate bank of the importer, so for simplicity, I considered collecting and presenting banks as the same.
The process is similar. The collecting bank will transfer the further documents to the presenting bank, So once the remitting bank checked the documents, they will transfer the documents to the collecting/presenting bank, When the documents arrive, meanwhile, the goods also arrive at the port So let’s call it arrival port, It is there in the importer’s country, If we talk about India, these goods will reach at a port in India, Till then the documents will reach the collecting/presenting bank, Keep this in mind that the goods reached the port but not to the importer, The importer will only get the delivery of the goods, when he will present the documents, Thats why I said that the bill of lading is very important.
A receipt for the goods. In fact, the title of the goods, Until the importer will not present the documents of this title on the port, till then, he’ll not get the delivery. So, till the process is same, we saw the 4 steps sales contract, goods shipped On 3rd, the documents reached the remitting bank from the exporter, and then to the collecting bank, Till the process is the same in both D/P and D/A.
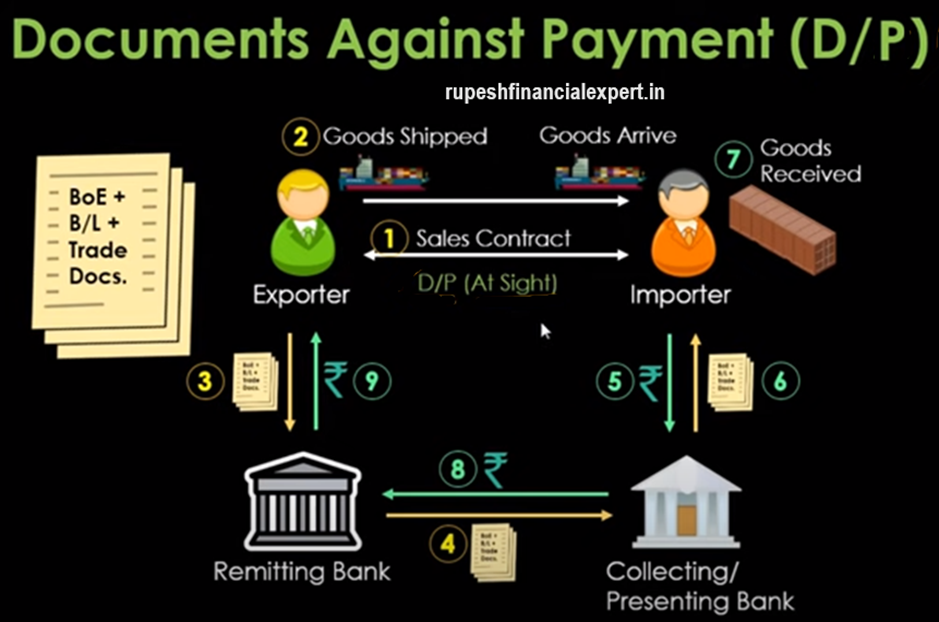
Now let’s understand that in the case of Documents against Payment (D/P), So how does this process works in the case of D/P, So as I said earlier, this is an at sight bill or demand bill, So as the collecting bank will present this bill of exchange in front of the importer, then importer has to do the payment immediately, So as the bill of exchange will be presented in front of the importer, he has to do the payment first, After doing the payment, he’ll get the documents in the next step, That’s why it is called documents against payment, So first he will do the payment and then he’ll get the documents, Importer goes with document against payment, when he doesn’t want credit period.
So till the time goods will arrive, he’ll arrange the payment, Once he gets the documents, he will present those at the port, And in the 7th step, he will receive the goods, Once he received the goods, at the same time The collecting/presenting bank will transfer the money to the remitting bank, And in the final step, the remitting bank will transfer the money to the exporter. So this was the process of documents against payment.
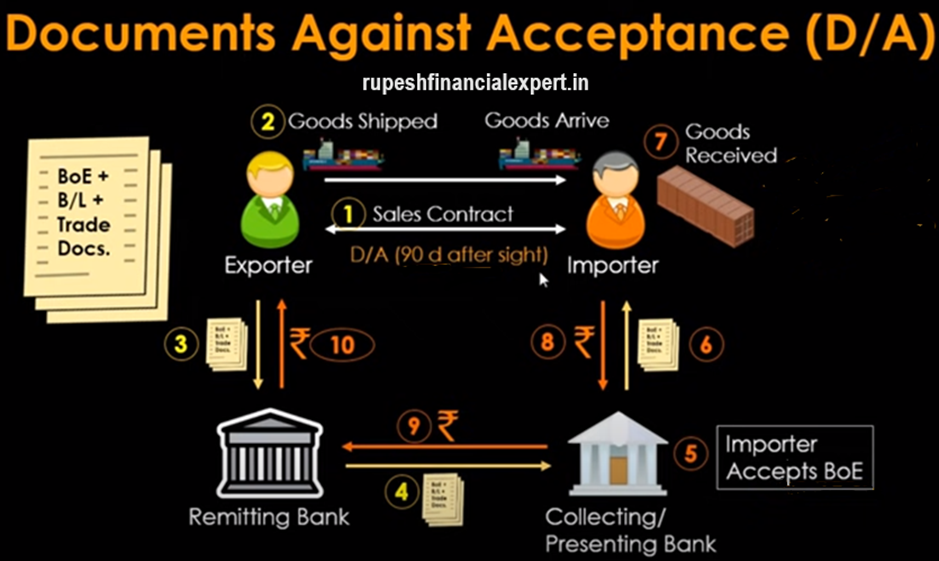
Now let’s see what the difference in Documents against Acceptance is (D/A) , the credit period of 90 days after sight is given, That means the importer will do the payment 90 days, after he will accept the bill of exchange, He got a credit period of 90 days, As we saw in the documents against payment, the importer has to do immediate payment to the presenting bank.
In this case, firstly, the importer will accept and sign the bill of exchange to show, that he accepted the credit period of 90 days, and will do the payment after 90 days, So once he accepted, the documents will be handed over in the 6th step, After the documents will be handed over, he will present them at the port, and he will receive the goods, When the goods will be received, he will send the goods to the retailers, Because he doesn’t have to do the payment immediately, so let’s say this is retailer 1, retailer 2, He has multiple retailers, When he will send the goods to the retailers, in exchange, he will start getting the payments, also he’ll start getting the payments 1, 2, and 3, Maybe the payment cycle for them is less than 90 days.
So when he’ll receive all the payments, he will transfer the money after 90 days to the presenting bank, or to the collecting bank, Once the collecting/presenting bank will receive money after 90 days, that money will be transferred to the remitting bank. and the remitting bank will finally transfer it to the exporter, under documents against acceptance, there is a credit period, and that’s why we call it Usance bill or time bill, And in documents against payment, immediate payment is to be done.
I think I covered the process flow of both documents against payment and documents against acceptance, If you liked this blogs, then do like it and share it with your friends and family members, So that they can also get the benefit out of this blogs, If you have any suggestions or if you want to give any feedback related to his website, Then you can comment down below In fact, you can suggest topics for future blogs, I read all of your comments regularly so comment down the topics I should cover. because I keep bringing these informative finance related blogs daily.
So, we’ll meet in the next blogs. Till then keep learning, keep earning, and stay happy as always.